Blog
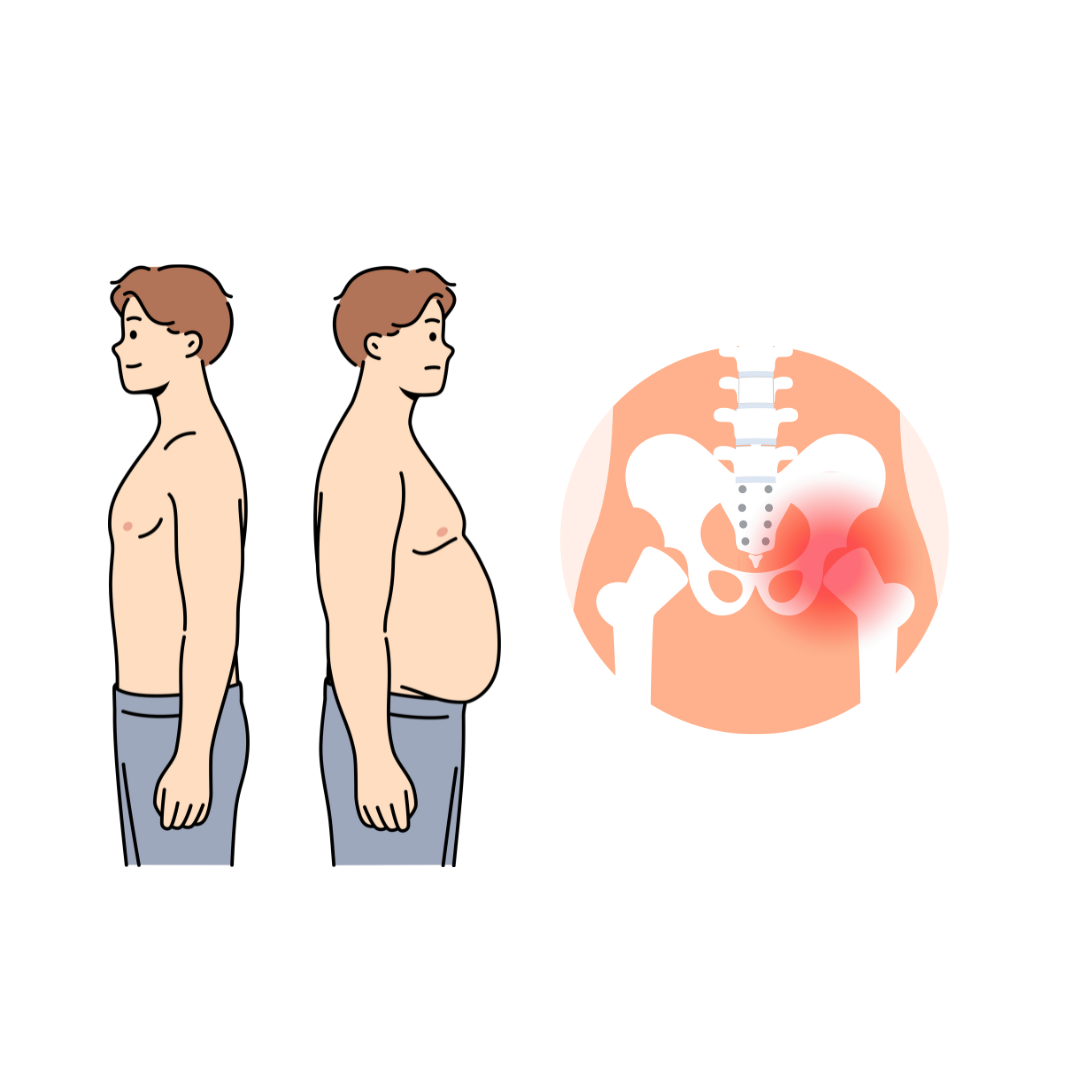
Why Weight Loss May Not Reduce Hip Osteoarthritis Pain
New research shows that for people with hip osteoarthritis, losing weight through a very-low-calorie diet combined with exercise does not reduce hip pain more than exercise alone, even if they are overweight. While both groups experienced less pain after six months, the extra weight loss didn’t lead to significantly better pain relief. This is different from knee osteoarthritis, where weight loss can make a bigger difference. Experts believe this is because hip pain is more related to the shape and structure of the hip joint itself. So, for those with hip OA, staying active with exercise is important, but losing weight might not reduce pain as much as expected. This information could also help patients and doctors decide when surgery might be the best option without delaying for weight loss first.
Read More
Health Canada Warns Against Unauthorized Injectable Peptides Sold Online
Health Canada is warning the public about the serious health risks of using unauthorized injectable peptide drugs, which are often promoted online for muscle building, weight loss, anti-aging, or athletic performance. These products—sold through websites like the now offline "Canada Peptide"—have not been approved for use in Canada and may lead to harmful side effects such as infections, allergic reactions, or dangerous interactions with other medications. Health Canada urges people not to buy or use these drugs and to dispose of them safely through a pharmacy or local hazardous waste program. To stay safe, always check for an official Drug Identification Number (DIN), Natural Product Number (NPN), or Homeopathic Drug Number (DIN-HM) on the label, and only purchase prescription medications from licensed pharmacies.
Read More
FDA Approves First Nerve-Stimulating Implant to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis Without Drugs
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the first-ever device to treat an autoimmune condition using nerve stimulation. Designed for people with rheumatoid arthritis, the tiny implant is placed in the neck alongside the vagus nerve—an important nerve that connects the brain to major organs. Once a day, it sends gentle electrical pulses that help calm the body’s immune response and reduce inflammation. Unlike traditional medications that suppress the immune system and often cause side effects, this device offers a drug-free approach that can ease joint pain and swelling without raising the risk of infections. Many patients in clinical trials were able to stop their usual medications entirely, offering new hope for people living with chronic autoimmune diseases.
Read More
FDA Approves First Nerve-Stimulating Implant to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis Without Drugs
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the first-ever device to treat an autoimmune condition using nerve stimulation. Designed for people with rheumatoid arthritis, the tiny implant is placed in the neck alongside the vagus nerve—an important nerve that connects the brain to major organs. Once a day, it sends gentle electrical pulses that help calm the body’s immune response and reduce inflammation. Unlike traditional medications that suppress the immune system and often cause side effects, this device offers a drug-free approach that can ease joint pain and swelling without raising the risk of infections. Many patients in clinical trials were able to stop their usual medications entirely, offering new hope for people living with chronic autoimmune diseases.
Read More
The Role of AI in Chronic Pain Research
In our latest episode of the Chronic Pain Chronicles, we had the privilege of speaking with a globally recognized expert in neurosurgery and brain imaging: Dr. Antonio Di Ieva. This episode dives deep into the complex world of the human brain—how we map it, treat it, and even predict its behavior using the latest advancements in artificial intelligence. Dr. Di Ieva is a neurosurgeon and neuroscientist with a passion for unraveling the brain’s structure-function relationship. He has pioneered research in fractal geometry in neuroscience and is a leader in applying machine learning to medical imaging. In this conversation, we explored not only the cutting-edge technologies transforming neurosurgical practice but also how these innovations may offer new hope for patients dealing with chronic neurological pain.
Read More