Blog
Karmy Clinic Explores Nerve Blocks in the Management of Fibromyalgia: A Case Report
This case report highlights a new approach to managing fibromyalgia-related pain using targeted nerve blocks. A 45-year-old woman with severe neck and shoulder pain saw significant relief after receiving weekly injections that numbed specific nerves. Her pain dropped from a 9 to a 2 on the pain scale, allowing her to move more easily and improve her daily life over six months. This suggests that nerve blocks may help reduce pain signals and improve symptoms in fibromyalgia patients, especially those with muscle-related pain. While more research is needed, this treatment could be a valuable option alongside other pain management strategies.
Read More
Cannabis Legalization Linked to Rise in Schizophrenia Cases
A new study from Ontario, Canada, suggests that cannabis legalization may be linked to a rise in schizophrenia cases, particularly among young men. Researchers found that hospital visits for cannabis use disorder (CUD) increased by 270% after legalization, and the proportion of schizophrenia cases associated with CUD nearly tripled. While the study does not prove that cannabis directly causes schizophrenia, experts warn that regular use—especially of high-potency strains—can worsen symptoms and lead to earlier onset in those predisposed to the condition. Public health experts emphasize the need for better awareness, as many people underestimate the risks of cannabis, thinking that its legal or medical status makes it completely safe. Like alcohol and tobacco, cannabis carries potential health consequences, and experts recommend ongoing research and education to help people make informed choices.
Read More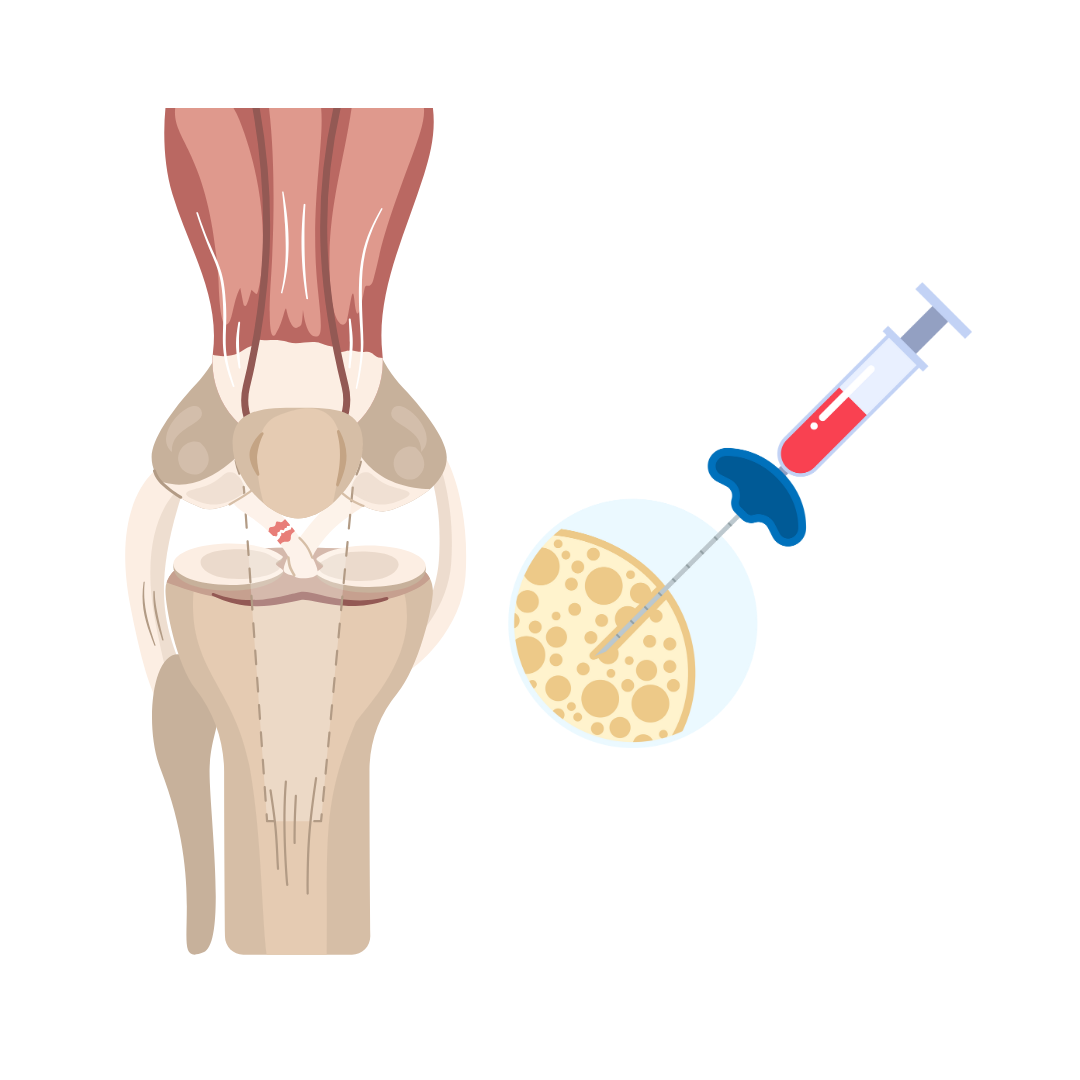
Can Your Own Bone Marrow Help Prevent Arthritis After ACL Surgery?
Researchers at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City are investigating whether concentrated bone marrow aspirate (cBMA), a therapy derived from a patient’s own bone marrow, can help reduce the risk of arthritis after ACL revision surgery. Many young athletes who suffer ACL injuries face a high chance of developing posttraumatic osteoarthritis (OA) years later, even after successful surgery. This study aims to see if cBMA can reduce inflammation, speed up recovery, and protect the knee joint from long-term damage. By tracking pain levels, inflammation markers, and knee function over two years, researchers hope to find a way to improve outcomes for patients at risk of developing arthritis after sports injuries.
Read More
Update: FDA Approves Suzetrigine: A New Non-Opioid Painkiller for Acute Pain Relief
The FDA has approved a new non-opioid pain medication called suzetrigine (Journavx) for adults with moderate-to-severe acute pain. Unlike traditional painkillers, suzetrigine works by blocking a specific pain pathway in the nerves outside the brain, providing relief without the risk of addiction associated with opioids. Clinical trials showed that it effectively reduced pain after surgeries like abdominoplasty (tummy tuck) and bunion removal. Common side effects include itching, muscle spasms, and mild skin reactions. This approval marks an important step in offering safer, effective alternatives for pain management.
Read More
Craniosacral Therapy: A Gentle Approach to Chronic Pain Relief
Craniosacral therapy (CST) is a gentle, hands-on technique designed to relieve tension in the body’s connective tissue, known as fascia. Practitioners use light touch to help promote relaxation, pain relief, and overall well-being. Many people seek CST for conditions like chronic pain, migraines, fibromyalgia, and stress-related tension. While some individuals report feeling immediate relief, others may need multiple sessions to experience the full benefits. Though research on its effectiveness is ongoing, CST is generally considered safe when performed by a trained professional. If you're curious about alternative therapies for pain or relaxation, talking to a healthcare provider can help determine if CST is right for you.
Read More